Metallic material
Innovation | Professionalism
Integrity | Efficiency
Metallic material
Innovation | Professionalism
Integrity | Efficiency
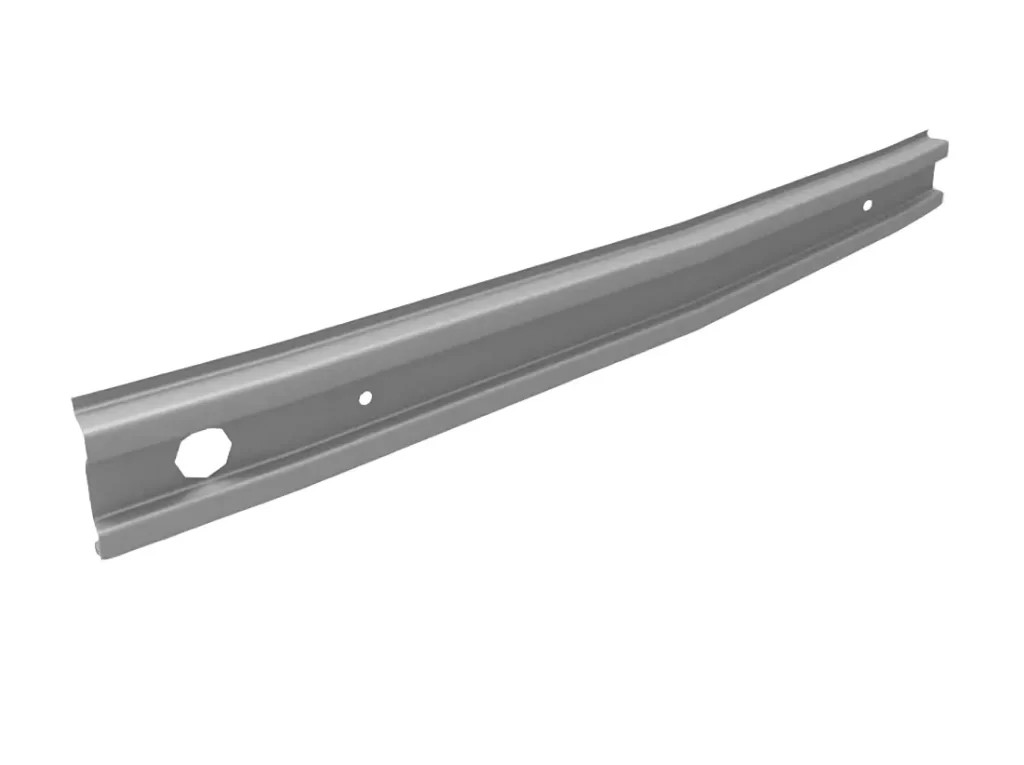
A rear anti-collision beam, also known as a rear bumper beam or rear impact bar, is an essential component of a vehicle’s rear-end collision protection system. It is a metal bar located behind the rear bumper and is designed to absorb and dissipate the energy generated during a rear-end collision, thereby reducing the force of impact transferred to the vehicle’s occupants.
The rear anti-collision beam is typically made of steel or aluminum and is bolted to the vehicle’s frame or body. It is engineered to withstand various types of impact forces and to distribute the energy evenly throughout the vehicle’s structure, thus minimizing damage to the vehicle’s rear end.
In addition to its impact-absorbing function, the rear anti-collision beam also serves as a mounting point for other rear-end components such as the rear bumper cover and taillights. It is an integral part of the vehicle’s overall design and plays a crucial role in protecting the occupants during a rear-end collision.
Martensitic steel is a type of steel that is characterized by its high strength and hardness. This steel is obtained by quenching the steel after cold rolling and continuous annealing, which results in the formation of a large amount of martensite structure. Martensite is a type of crystal structure that is formed during the cooling process of steel. It is a very hard and brittle structure that provides high strength to the steel.
The process of obtaining martensitic steel involves heating the steel to a high temperature and then rapidly cooling it by quenching it in a liquid such as water or oil. This rapid cooling process prevents the steel from undergoing the usual slow cooling process in the instead Austenitic structure, resulting in the formation of a high concentration of martensite.
The main organization of martensitic steel is lath martensite. Lath martensite is a specific form of martensite that is characterized by a lath-like structure. This structure is formed when the steel is rapidly cooled from a high temperature, causing the austenitic structure to transform into the martensitic structure. The lath martensitic structure is responsible for the high strength and hardness of martensitic steel.
| Grade | YS(MPa) | TS(MPa) | EL(%) | r | n | BH2(MPa) |
| HC1350/1700MS | 1350-1700 | ≥1700 | ≥3% | – | – | – |
Grade: HC1350/1700MS
C(max): 0.35
Mn(max): 3
Si(max): 1
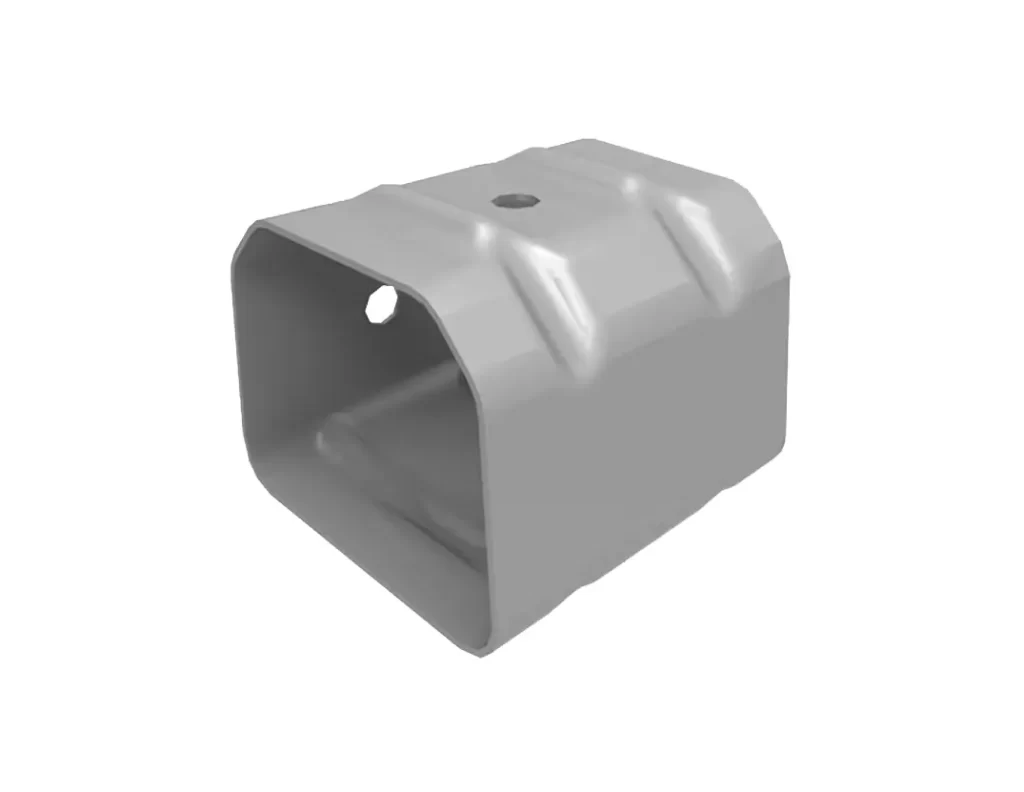
The Rear Crash Absorption Box for Bumper Beam is an important auto part that is designed to absorb impact and minimize damage during rear-end collisions. It is typically located behind the rear bumper and is made from a combination of materials, such as steel and plastic, to provide both strength and flexibility.
During a rear-end collision, the Rear Crash Absorption Box for Bumper Beam absorbs the energy of the impact and redirects it away from the passengers and the vehicle’s frame. This helps to prevent damage to the vehicle’s body and reduces the risk of injury to the occupants.
In addition to its protective function, the Rear Crash Absorption Box for Bumper Beam also helps to improve the overall aerodynamics of the vehicle, which can enhance its performance and fuel efficiency.

Low-alloy high-strength steel is a type of steel that contains small amounts of alloying elements such as niobium, titanium, and vanadium. These elements are added singly or in combination to low-carbon steel to form carbon and nitrogen compound particles for precipitation . These particles help to strengthen the steel, making it more durable and resistant to deformation.
In addition to strengthening the steel, microalloying elements also refine the grain structure of the steel. This refinement leads to a more uniform distribution of the alloying elements and helps to prevent the formation of large, brittle grains. The result is a steel that is both Strong and ductile, meaning it can withstand high levels of stress without breaking or deforming.
One of the advantages of low-alloy high-strength steel is its good weldability. This means that it can be easily welded without compromising its strength or durability. This makes it a popular choice for applications where welding is necessary, such as in the construction of bridges, buildings, and pipelines.
The microstructure of low-alloy high-strength steel is typically composed of ferrite and a small amount of carbide. Ferrite is a type of iron that is relatively soft and ductile, while carbide is a hard, brittle compound that contains carbon and other elements. The combination of these two materials results in a steel that is strong, ductile, and highly resistant to deformation and wear.
| Grade | YS(MPa) | TS(MPa) | EL(%) | r | n | BH2(MPa) |
| HC340LAD+Z | 340-420 | 410-510 | ≥21% | – | – | – |
Grade: HC340LAD+Z
C(max): 0.11
Mn(max): 1
Si(max): 0.5
Our company: Hengqiao(Shanghai) International Trading Limited
The company’s main business is general GMW standard, Fiat EFE standard, Volvo VDA standard, Nissan NEN standard, Volkswagen VW50065, Ford WSS-M and other standard series of automotive steel.
Looking forward to your inquiry!

We are looking forward to your message:
Send RequestFind your contact person directly here:
To our locations