Metallic material
Innovation | Professionalism
Integrity | Efficiency
Metallic material
Innovation | Professionalism
Integrity | Efficiency
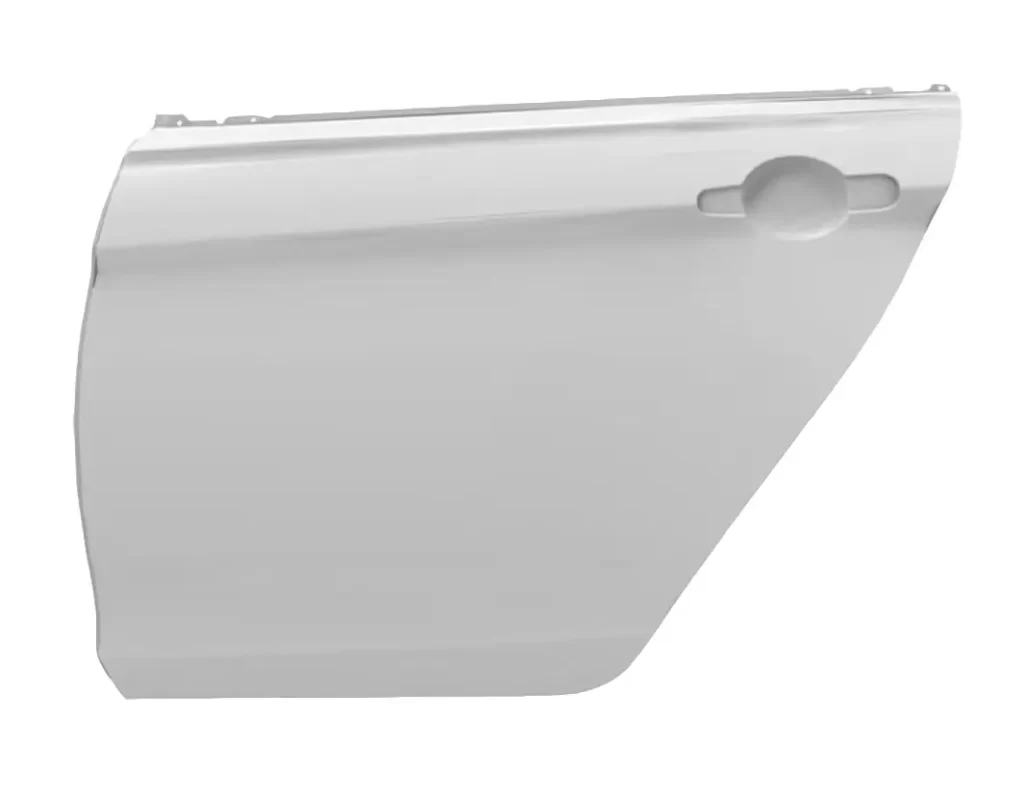
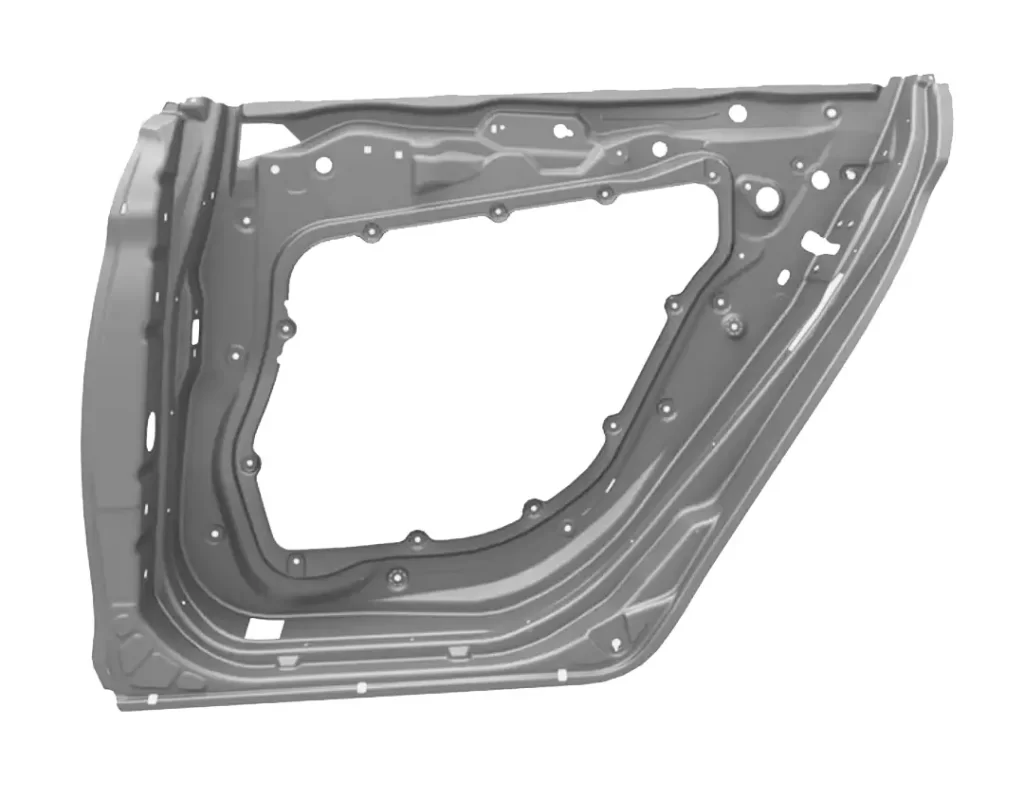
The back door outer panel is a component of a vehicle’s rear hatch or trunk that provides structural support, protects the inner components of the door, and helps maintain the aerodynamics of the vehicle. It is typically made of steel, aluminum, or other durable materials that can withstand impacts and resist corrosion.
The back door outer panel is designed to fit precisely with the rest of the rear hatch or trunk components and may include features like mounting points for hinges, latches, and other hardware. If the back door outer panel is damaged, it can compromise the integrity of the rear hatch or trunk, making it difficult to open or close properly and affecting the safety of the vehicle’s occupants in the event of a collision.

The strength of steel is influenced by several factors, including the presence of carbon and nitrogen atoms, which can form solid solutions within the steel. These atoms can increase the strength of the steel by reducing the movement of dislocations, which are defects in the crystal structure of the metal. However, excessive amounts of carbon can also make the steel brittle.
To further enhance the strength of steel, strengthening elements such as phosphorus and manganese can be added. These elements can form interstitial solid solutions with the iron atoms, leading to an increase in the hardness and strength of the steel.
Once the steel has been processed and formed into its desired shape, it is typically baked at a specific temperature to further increase its strength through a process known as age hardening. During age hardening, the steel is heated to a specific temperature and held there for a period of time. This allows for the precipitation of small particles within the steel that act to inhibit the movement of dislocations, further increasing the strength of the material.
Steel that has undergone this process is commonly used in automotive outer coverings, which require high strength and durability. The organization of the steel is typically ferrite, a type of iron that is relatively soft and ductile, but can be hardened through the addition of other elements and heat treatments.
| Grade | YS(MPa) | TS(MPa) | EL(%) | r | n | BH2(MPa) |
| HC220BD+Z | 220-280 | 340-400 | ≥32% | ≥1.2 | ≥0.15 | ≥30 |
| HC220BD+ZF | 220-280 | 340-400 | ≥30% | ≥1 | ≥0.15 | ≥30 |
Grade: HC220BD+Z, HC220BD+ZF
C(max): 0.06
Mn(max): 1
Si(max): 0.5
The rear door outer panel reinforcement plate is a specific type of auto part that is designed to provide additional strength and protection to the outer panel of the rear door of a vehicle. It is typically made from durable materials, such as steel or aluminum, and is designed to withstand the harsh elements and the wear and tear of regular use.
In addition to its structural function, the rear door outer panel reinforcement plate can also provide added security for the vehicle. By strengthening the outer panel of the rear door, it can help to deter potential theft or damage.
Overall, the rear door outer panel reinforcement plate is an important auto part that helps to ensure the safety, durability, and security of a vehicle.
The microstructure of a material refers to the arrangement of its constituent particles or grains, and in this particular case, the material being referred to consists mainly of ferrite and martensite. The martensite structure is dispersed in the ferrite in the form of islands on the substrate, which means that the martensite forms small, isolated regions within the larger ferrite structure.
Dual phase steels are a type of steel that have been specifically designed to have a microstructure consisting of both ferrite and martensite. This microstructure gives them several desirable properties, including a low yield ratio and a high work hardening exponent. The yield ratio refers to the ratio of the yield stress to the tensile strength of a material, and a low yield ratio indicates that the material can undergo more deformation before it reaches its yield point. The work hardening exponent measures how much a material’s strength increases as it is deformed, and a high work hardening exponent indicates that the material can be easily formed into complex shapes.
In addition to these properties, dual phase steels also exhibit a phenomenon known as bake hardening, which refers to an increase in strength that occurs when the material is heated and then cooled. This makes them ideal for use in automotive structural parts, as these parts need to be able to withstand high levels of stress and deformation without failing.
| Grade | YS(MPa) | TS(MPa) | EL(%) | r | n | BH2(MPa) |
| HC340/590DPD+Z | 290-370 | ≥500 | ≥27% | – | ≥0.15 | – |
Grade: HC340/590DPD+Z
C(max): 0.15
Mn(max): 2.5
Si(max): 0.6
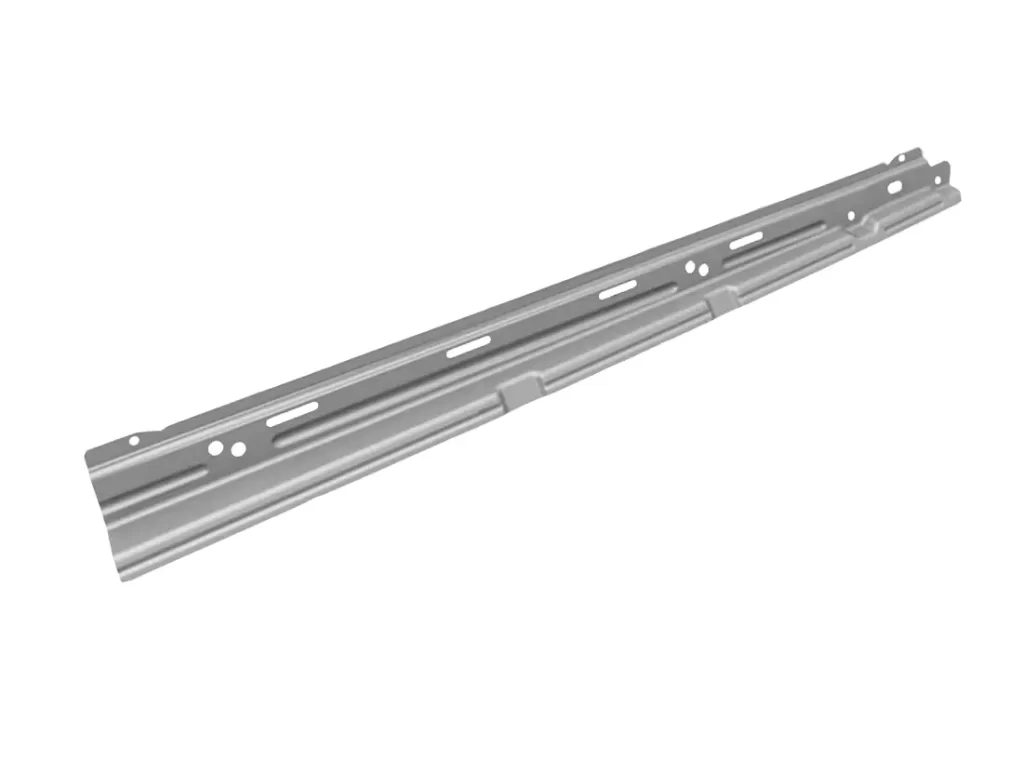
The rear door anti-collision beam is an automotive part that is designed to provide additional protection to the rear of a vehicle in the event of a collision. It is typically installed on the rear doors of a vehicle and is constructed of heavy-duty materials such as steel.
The purpose of the rear door anti-collision beam is to absorb the impact of a collision, distributing the force of the impact across a wider area and minimizing the damage to the vehicle. In particular, it helps to protect the rear passengers of the vehicle from injury by absorbing the energy of a rear-end collision.
In addition to its safety benefits, the rear door anti-collision beam can also provide added structural support to the rear of the vehicle. This can help to improve the overall durability and longevity of the vehicle.

The microstructure of a material refers to the arrangement of its constituent particles or grains, and in this particular case, the material being referred to consists mainly of ferrite and martensite. The martensite structure is dispersed in the ferrite in the form of islands on the substrate, which means that the martensite forms small, isolated regions within the larger ferrite structure.
Dual phase steels are a type of steel that have been specifically designed to have a microstructure consisting of both ferrite and martensite. This microstructure gives them several desirable properties, including a low yield ratio and a high work hardening exponent. The yield ratio refers to the ratio of the yield stress to the tensile strength of a material, and a low yield ratio indicates that the material can undergo more deformation before it reaches its yield point. The work hardening exponent measures how much a material’s strength increases as it is deformed, and a high work hardening exponent indicates that the material can be easily formed into complex shapes.
In addition to these properties, dual phase steels also exhibit a phenomenon known as bake hardening, which refers to an increase in strength that occurs when the material is heated and then cooled. This makes them ideal for use in automotive structural parts, as these parts need to be able to withstand high levels of stress and deformation without failing.
| Grade | YS(MPa) | TS(MPa) | EL(%) | r | n | BH2(MPa) |
| HC820/1180DPD+Z | 820-1150 | ≥1180 | ≥6% | – | – | – |
Grade: HC820/1180DPD+Z
C(max): 0.23
Mn(max): 3
Si(max): 1
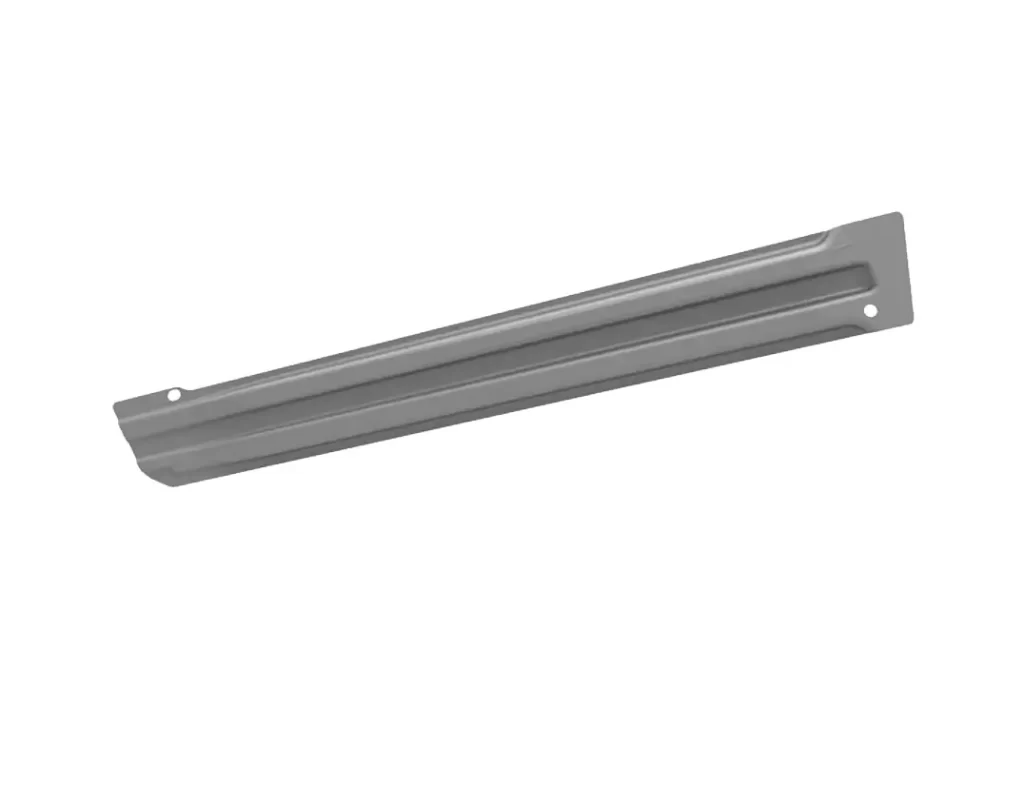
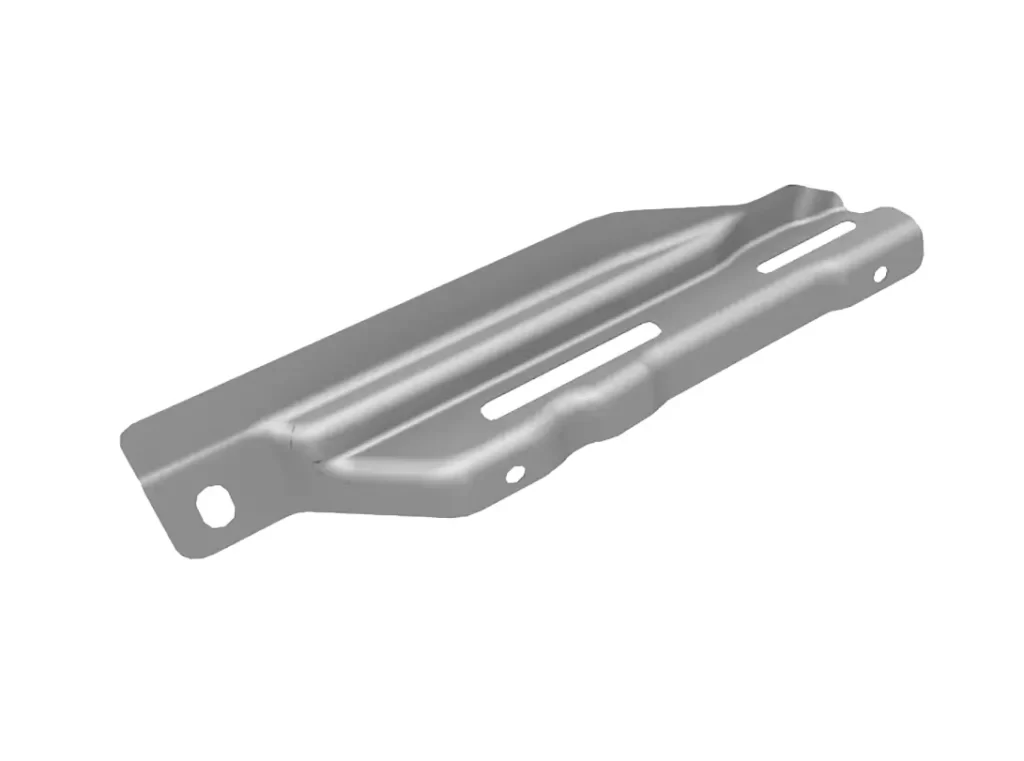
The rear door triangle glass support board is an automotive part that is used to support the triangular piece of glass that is typically found in the rear doors of certain vehicles, such as SUVs or minivans. It is typically made from a durable material such as plastic or metal, and is designed to securely hold the glass in place.
The purpose of the rear door triangle glass support board is to provide additional structural support to the rear door and help to keep the glass securely in place. This is important for both safety and functionality, as a loose or improperly supported piece of glass could pose a hazard to both the driver and passengers of the vehicle.
Carbon structural high-strength steel is a specific type of steel that is used in a variety of applications, including automotive manufacturing, construction, and engineering. This type of steel is designed to provide a high level of strength and durability, while maintaining a relatively lightweight and cost-effective construction.
One of the key features of carbon structural high-strength steel is its ability to achieve high strength through the addition of trace alloy elements such as silicon (Si) and manganese (Mn). These elements are added to the steel during the manufacturing process, and help to improve the material’s strength and hardness through a process known as solid solution strengthening.
The main structure of carbon structural high-strength steel is typically a combination of ferrite and pearlite. Ferrite is a type of iron that is relatively soft and ductile, while pearlite is a combination of ferrite and cementite that is harder and more brittle. The combination of these two structures helps to provide a balance of strength, toughness, and ductility that is well-suited for a wide range of applications.
| Grade | YS(MPa) | TS(MPa) | EL(%) | r | n | BH2(MPa) |
| B280VK | 280-400 | ≥440 | ≥29% | – | – | – |
Grade: HC820/1180DPD+Z
C(max): 0.15
Mn(max): 2
Si(max): 0.5
The rear door inner panel is a component of a vehicle’s door assembly that is located on the inside of the rear door. It is typically made of plastic or a similar material and is designed to provide structural support to the door and serve as a mounting point for various components.
The rear door inner panel is an essential part of the door assembly, as it provides a surface for the installation of the window regulator, door handle, and other components that are necessary for the door’s operation. It is also designed to help reduce noise and vibration by providing a barrier between the interior of the vehicle and the outside environment.
Mild steel is a type of steel that is commonly used in a wide variety of applications due to its properties. It can be divided into two categories: ordinary low-carbon steel and interstitial atom-free steel. The microstructure of mild steel is typically ferrite , which is a type of iron crystal that is known for its softness and ductility. Ordinary low-carbon steel may also contain a small amount of pearlite, which is a mixture of ferrite and cementite.
Despite its low strength and hardness, mild steel is prized for its stamping and welding properties. Its low carbon content makes it easy to work with and shape, which makes it a popular choice for a range of industrial applications. Additionally, interstitial-free steel is particularly well-suited for stamping complex, deep-drawn parts such as body side panels, door inner panels, floor parts, and fuel tanks.
| Grade | YS(MPa) | TS(MPa) | EL(%) | r | n | BH2(MPa) |
| DC54D+Z-T | 120-200 | 260-350 | ≥36% | ≥1.8 | ≥0.2 | – |
Grade: DC54D+Z-T
C(max): 0.12
Mn(max): 0.6
Si(max): 0.5
Our company: Hengqiao(Shanghai) International Trading Limited
The company’s main business is general GMW standard, Fiat EFE standard, Volvo VDA standard, Nissan NEN standard, Volkswagen VW50065, Ford WSS-M and other standard series of automotive steel.
Looking forward to your inquiry!

We are looking forward to your message:
Send RequestFind your contact person directly here:
To our locations