Explore Ferritic Stainless Steels
2023-03-27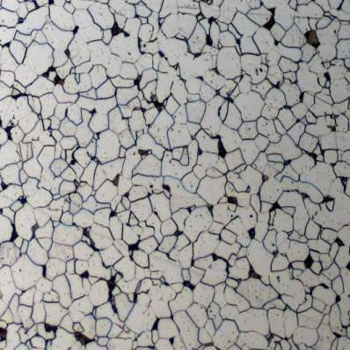
Ferritic stainless steel is a type of stainless steel whose microstructure consists mainly of the ferrite phase. Ferrite is a crystalline structure, usually face-centered cubic, that is the most stable phase of iron at room temperature. The main components of ferritic stainless steel are iron, chromium and carbon, of which the content of chromium is usually between 12-30%, and the content of carbon is less than 0.2%.
The main characteristics of ferritic stainless steel are excellent corrosion resistance, magnetism and processability. Compared with austenitic stainless steel, ferritic stainless steel is easier to process and form, and has higher strength and hardness. However, its corrosion resistance is not as good as that of austenitic stainless steel, especially in high temperature and acidic environments, which are prone to corrosion.
How high temperature can ferritic stainless steel withstand?
The high-temperature stability of ferritic stainless steel depends on factors such as its specific composition, microstructure and service conditions. Generally speaking, ferritic stainless steel can withstand high temperature at room temperature, but when the temperature rises, its strength, hardness and corrosion resistance will gradually decrease, so it is necessary to select the appropriate ferritic stainless steel material according to the specific use conditions .
The limit service temperature of some common ferritic stainless steels at high temperature is as follows:
● 430 stainless steel: It can be used below 800℃, but the higher the temperature, the worse its corrosion resistance.
● 446 stainless steel: It has good oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance at high temperature, and can be used at a temperature up to 1150 °C.
● 409 stainless steel: It can be used in the temperature range of 600-750℃.
It should be noted that when ferritic stainless steel is used at high temperature, the use of oxidizing acid, chloride and other media with too high concentration should be avoided, so as not to accelerate its corrosion rate.
Is ferritic stainless steel brittle?
Under certain conditions, ferritic stainless steels may be more brittle than other types of stainless steels such as austenitic stainless steels. This is because ferritic stainless steels have a body-centered cubic (BCC) crystal structure, which is more prone to brittle fracture than the face-centered cubic (FCC) crystal structure of austenitic stainless steels.
The brittleness of ferritic stainless steel is affected by factors such as temperature, stress and the presence of defects or impurities. The presence of stress can also increase susceptibility to brittle fracture, especially in the presence of hydrogen or other environmental factors.
However, not all ferritic stainless steels are inherently brittle, and many grades have good ductility and toughness. The degree of brittleness depends on the specific grade of ferritic stainless steel, its composition and service conditions. Therefore, it is important to carefully consider the specific application and select the appropriate grade of ferritic stainless steel for the intended use to ensure adequate mechanical properties and resistance to brittle fracture.
Can ferritic stainless steel be quenched?
Generally speaking, ferritic stainless steel cannot improve its hardness and strength by traditional quenching methods such as water quenching or oil quenching, because its microstructure is prone to phase transformation during cooling, resulting in increased brittleness and crack sensitivity of the material , and may cause hydrogen embrittlement. Therefore, traditional quenching methods are generally not used for heat treatment of ferritic stainless steel in production.
Is ferritic stainless steel suitable for kitchen utensils?
Ferritic stainless steel can be suitable for some kitchen utensils, but it may not be the best choice for all applications. For example, ferritic stainless steel may be a good choice for items such as sinks, range hoods and oven linings that require good heat and corrosion resistance. However, ferritic stainless steels may not be the best choice for items such as knives or other cutting implements due to their need for high hardness and edge retention. Ferritic stainless steels are generally softer than martensitic or austenitic stainless steels and may not hold an edge as well, making them less suitable for cutting applications.
The suitability of ferritic stainless steels for kitchen utensils depends on the application and the properties required for the intended use. It is important to carefully consider specific requirements and select the appropriate grade of stainless steel for the application to ensure optimum performance and durability.
What are common ferritic stainless steels?
Typical grades of ferritic stainless steels are:
409 stainless steel – widely used in automotive exhaust system components such as mufflers, catalytic converters, center pipes and tailpipes.
430 stainless steel——Widely used in interior decoration, daily office equipment, kitchen equipment, household appliances, etc., is the brand with the largest output of ferritic stainless steel.
439 stainless steel——Mainly used in automobile exhaust system mufflers, but also widely used in household appliances, washing machine inner barrels, gas, water heaters, exchangers, low-voltage feed water heaters for power stations, etc.
Are there any downsides to ferritic stainless steel?
Ferritic stainless steel has good corrosion resistance, heat resistance and processing performance, but there are also some shortcomings, mainly including the following aspects:
1. Poor low-temperature toughness: The low-temperature toughness of ferritic stainless steel is not as good as that of austenitic stainless steel, and it is prone to brittle cracking in low-temperature environments, so special attention should be paid when using it in low-temperature conditions.
2. Susceptible to pitting corrosion and intergranular corrosion: In an environment containing chloride ions and chlorides, ferritic stainless steel may undergo pitting corrosion and intergranular corrosion, which will affect the corrosion resistance of the material.
3. Not suitable for high-concentration acidic environment: Ferritic stainless steel has poor corrosion resistance to high-concentration acidic environment and is easy to be etched by acid, so special attention should be paid when using it in this environment.
To sum up, although ferritic stainless steel has many advantages, it is also necessary to select the appropriate material according to the specific application and requirements.
How to distinguish ferrite and austenite?
Ferrite and austenite are two different crystal structures that can exist in certain types of metals, including iron and steel. They have different physical and mechanical properties, so it’s important to be able to distinguish between them.
Here are a few ways to distinguish ferrite and austenite:
Magnetic properties: Ferrite is magnetic, while austenite is non-magnetic. If you have a magnet, you can use it to test whether a sample of metal is ferritic or austenitic.
Microstructure: Ferrite has a body-centered cubic (BCC) crystal structure, while austenite has a face-centered cubic (FCC) crystal structure. You can examine a sample of metal under a microscope to see its microstructure and determine whether it’s ferritic or austenitic.
Chemical composition: The chemical composition of the metal can also help you distinguish between ferrite and austenite. Ferrite has a higher concentration of iron and lower concentrations of carbon and other elements, while austenite has a lower concentration of iron and higher concentrations of carbon and other elements.
Heat treatment: Heat treatment can also affect the microstructure of metal and the presence of ferrite and austenite. For example, if a sample of steel is cooled slowly from a high temperature, it may form more austenite, while if it’s cooled quickly, it may form more ferrite.
Overall, these are some of the ways you can distinguish between ferrite and austenite in metals. It’s important to note that some metals may have a combination of ferritic and austenitic structures, which can affect their properties as well.
If you are looking for high-quality, durable and corrosion-resistant steel products, look no further than our company‘s ferritic stainless steels. Our ferritic stainless steels are an excellent choice for a wide range of applications, from automotive components to kitchen appliances. With their excellent corrosion resistance and attractive appearance, our ferritic stainless steels are a reliable and cost-effective choice for your manufacturing needs. Our company prides itself on providing exceptional customer service, ensuring you have the support and guidance you need to get the most out of our steel products. We also offer a range of machining and customization options including cutting, bending and welding to help you create the perfect product for your needs. Choose our ferritic stainless steels for your next project and experience the difference in quality and reliability.
